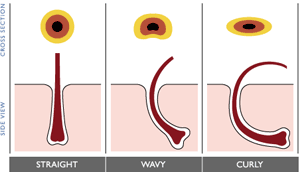
The texture of your hair is determined by the size and shape of the hair follicle, which is a genetic trait controlled by hormones and related to age and racial characteristics.
Whether hair is curly, wavy, or straight depends on two things - its shape as it grows out of the follicle and the distribution of keratin producing cells at the roots. Straight hair is formed by roots that produce same number of keratin cells all round the follicle.
The natural color of hair also affects the hair texture Natural blondes have finer hair than brunettes, while redheads have the thickest hair.
Generally speaking hair can be divided into three categories - fine, coarse and thick. Fine hair can be strong or weak, however because of its texture, all fine hair has the same characteristic - it lacks volume. As the name suggests, medium hair is neither too thick nor too thin, and is strong and elastic. Thick and coarse hair is abundant and heavy, with a tendency to grow outwards from the scalp as well as downwards. It often lacks elasticity and is frizzy.
A single head of hair may consists of several different textures. For example, fine hair is often found on temples, and the hairline at the front and on the nape of the head, while the texture over the rest of the head may be medium or even coarse.
Ethnic Differences and Hair Textures
Scandinavians normally have thin, straight, baby fine hair and mid-Europeans
have hair that is neither too fine nor too coarse. People native to the Indian
subcontinent have coarse textured tresses, while Middle-eastern populations
have strong hair. The hair of chinese and Japanese people is very straight
Hair Anatomy
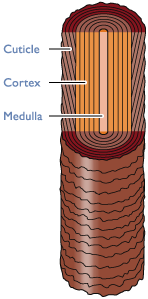
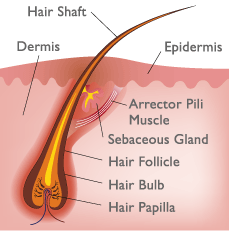 Hair is mainly composed of a protein called keratin (about 88%). Keratin starts out as a soft substance arising from the follicle and keratinizes (hardens) as it rises up and out into the hair shaft. Keratin is insoluble, very tough, and highly elastic. The Follicle is an indentation that pushes down into the deep layers of the skin, and is where keratin develops. The Sebaceous gland is the individual hair’s well of natural oil. Too much or two little production of oil from this gland can cause symptoms of oiliness or dryness in the hair and scalp. | Cuticle
Cortex Medulla In general, hair exists as one of these three shapes. As it grows, the hair shaft assumes the shape, size and direction of the follicle. |